Weekly Blog 1- Hamed Saleh AL Foori
Background
This
exercise is part of the PMP course, which is a three months program started on November
29th , 2017 and conducted by Dr. Paul D. Giammalvo from PT Mitrata
Citragraha. Engineers from the Oman Power and Water Procurement attended a face
to face session for a period of one week. The program was divided into four
projects to be completed during the upcoming three months, which include weekly
reports, weekly blogs, an academic paper and problem solving for the PMP exam
preparation. Following the face to face session is an online learning program
for the four assigned projects.
Problem Statement
The topic
of the blog for week (1) examines how the Future OPWP PMP 2017 team is
effective and what opportunities of improvement are there in order to achieve
the desired outputs of the program. The exercise in this blog will identify
which stage of Tuckman’s (4) stages of team development Future OPWP PMP 2017
fits in and possible plans for team improvements.
Assessment Results and Root
Cause Analysis
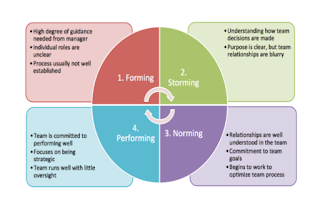
Tuckman’s
model was used to evaluate the stage in which the team fits in. This model
simply explained a team dedicated for a given project moves through four stages
before reaching high performance level. These stages are: forming, storming,
norming and performing. A survey established by Erin Barkema and John W. Moran
was used to carry out the assessment for the 13 members in the team to answer a
set of questions for each Tuckman’s stages. Analysis of the results are
presented in table 1.
Table 1:
Statistical Results of Tuckman’s Model
Average
|
Standard Deviation
|
|
Forming
|
23
|
2.1
|
Storming
|
20
|
1.6
|
Norming
|
30
|
4.7
|
Performing
|
31
|
6.2
|
The
survey showed a very positive overall result; the Future OPWP PMP 2017 team scored highest on the Performing stage,
with 31 points, followed by Norming, with 30 points. Because Norming stage has
lower standard deviation then performing, This indicates that we have created a
solid team with members being at the norming stage of Tuckman’s model
This
is due to the fact that team members know each other and some are team members
of the same department as following:
Figure 1: Problem Tree Analysis of the Survey’s Results
Feasible Alternatives
Because
the leadership style plays key rule, two leadership styles will be analyzed and
one option will be selected to support the results obtained from the
assessment.
Tools of Analyzing Different Leadership
Styles
Two
leadership styles were selected:
1- Autocratic Leadership: The leader has full authority and responsibility and make decisions
without consulting team members. Decisions from the boss are implemented with
little flexibility.
2- Coaching Leadership: The leader is involved in supervising the team members to ensure
high performance and better results. This leadership style creates skilled
staff and provides motivation to the team.
Selection of the Acceptable
Criteria
Pair-Wise
comparison is used to establish the important leadership attributes by
evaluating each attribute with a score of either 1 or 0. If the attribute on
the left column is more important than the one from corresponding row, the
score is 1, otherwise is 0.
Table 2:
Pair-Wise Comparison for Leadership Attributes
Leadership’s
Attributes
|
Teamwork
|
Skill Development
|
Authority to Act
|
Communication
|
Risk Control
|
Total
|
%
|
Teamwork
|
-
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
3
|
33.3 %
|
Skill Development
|
0
|
-
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
22.2 %
|
Authority to Act
|
0
|
0
|
-
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
22.2 %
|
Communication
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
-
|
1
|
2
|
22.2 %
|
Risk Control
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
Comparing the Outcomes form
Each Alternative
From
the pair-wise analysis, it turned out that the most important attribute is
teamwork, followed by skill development, authority to act, communication with
the same score and finally risk control.
Selection of the Best Leadership
Style
The
following table examines each attribute with the leadership style selected
previously to determine the best option. ( High = 2 , Medium =1, Low = 0)
Table 3:
Pair-Wise Comparison for Leadership Attributes with Leadership Styles
Attribute/Leadership
|
Teamwork (33.3 %)
|
Skill Development (22.2%)
|
Authority to Act (22.2%)
|
Communication (22.2%)
|
Risk Control ( 0 %)
|
Total
(score *%)
|
Autocratic
Leadership
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
1
|
2
|
1.21
|
Coaching
Leadership
|
2
|
2
|
0
|
2
|
1
|
1.54
|
From
the analysis above, we can conclude that coaching leadership style is better
than autocratic leadership style.
How to Track the Current Team Performance
The
team can track the performance of each project manager as well as the program
level based on the previous leadership attributes on a daily basis to examine
if the coaching leadership style is being implemented and what other
improvements the project and program managers could adopt in the upcoming days.
Reference:
Barkema, E., & Moran, J. W.
(2013, October). Retrieved from
http://www.phf.org/resourcestools/Documents/Electronic_Tuckman.pdf
Creating
a Pairwise Comparison Chart. (n.d.).
Retrieved from http://www.eahoover.com/dconn-web/EDP/Developing_a_PCC.pdf
European Integration Office. (n.d.). Guide to THE LOGICAL FRAMEWORK APPROACH.
Retrieved from
http://www.evropa.gov.rs/evropa/ShowDocument.aspx?Type=Home&Id=525
Tuckman
forming storming norming performing model.
(n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.businessballs.com/managing-teams/tuckman-forming-storming-norming-performing-model-234




WOW Haamed!!! Not only did you follow our 7 step process very well and met the TECHNICAL specifications by providing at least 3 references to support your analysis., but you also EXCEEDED expectations by combining Tuckman with a Problem Tree Analysis AND a Multi-Attribute Decision making model
ReplyDeleteVERY impressive....!!!
From this point on, you are free to pick any topic you wish, and show us how you are taking the tools/techniques you are learning in the PMBOK Guide or other references and are using them to generate a favorable Return on your Training Investment that OPWP is making in you.
BR,
Dr. PDG, Jakarta, Indonesia